Effective Hazards Analysis Steps¶
Hazard Identification and Evaluation with Risk Analysis and Assessment
Define the process
This step can involve collecting documentation such as a process flow diagram (PFD), piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID), operating procedure and other relevant information. It is also important to gather information about the process, such as the materials used, and the operating conditions among other things.
Identify the hazards analysis method to use
Hazards analysis methods include HAZOP, FMEA, and fault tree analysis (FTA). The choice of method will depend on the specific process and the goals of the analysis.
Identify the Hazardous Top Level Event and contributing factors with
a Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Including deductive and inductive reasoning
a HAZOP (Hazards and Operability Study)
Including guide words and deviations
Fill out a Hazards Analysis (HA) Table
For each failure mode (the lower level events in your falut tree anlaysis), fill out the hazards analysis table including the following information:
Task description or process step
Hazard type
Hazard description
Event consequence
Safeguards currently present to mitigate the hazard
Rank (1A to 5E) for severity and likelihood of the hazard
Recommendations to reduce the risk of the hazard
Potentially complete a quantitative risk analysis for those hazards with a high risk ranking
Incoporate other PSM elements per the OSHA 1910.119 standard

Figure 1:Effective Hazards Analysis Steps
Recommended Hazards Analysis Methods¶
The recommended methods for hazards analysis that we used effectively in evaluating explosive, pyrotechnic, and propellant based processes included:
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) with deductive and inductive reasoning followed by Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) where the HA table is filled out for each failure mode.
HAZOP (Hazards and Operability Study) with guide words and deviations
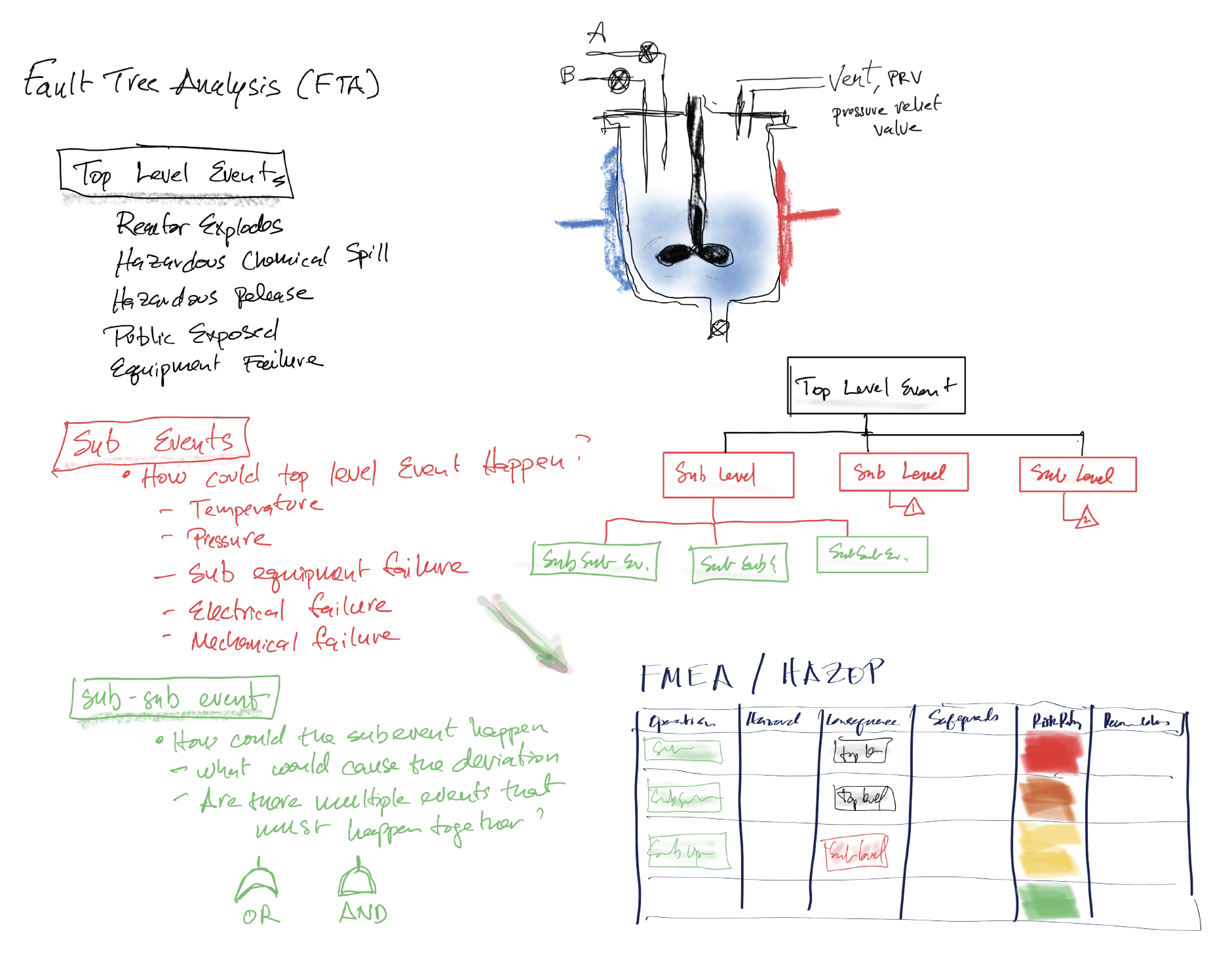
Figure 2:Fault Tree Analysis to Hazards Analysis Table
When Should you Conduct a Hazards Analysis? As early in the process as feasible.¶
Many complex processes have been designed and built prior to completion of a hazards anlysis (FTA with a FMEA, or HAZOP). This makes integration of engineering controls into the process very difficult or costly or both. Ideally you complete a hazards anlysis at the design stage and other stages including:
Design (a Design Hazards Analysis)
Construction and Startup
Operation
Decomissioning
Accident Investigation
Process Safety Information (PSI) is Critical¶
Process safety information including details of the process, the materials used, and the operating conditions is critical to completing a hazards analysis. We’ll talk a lot more about PSI.
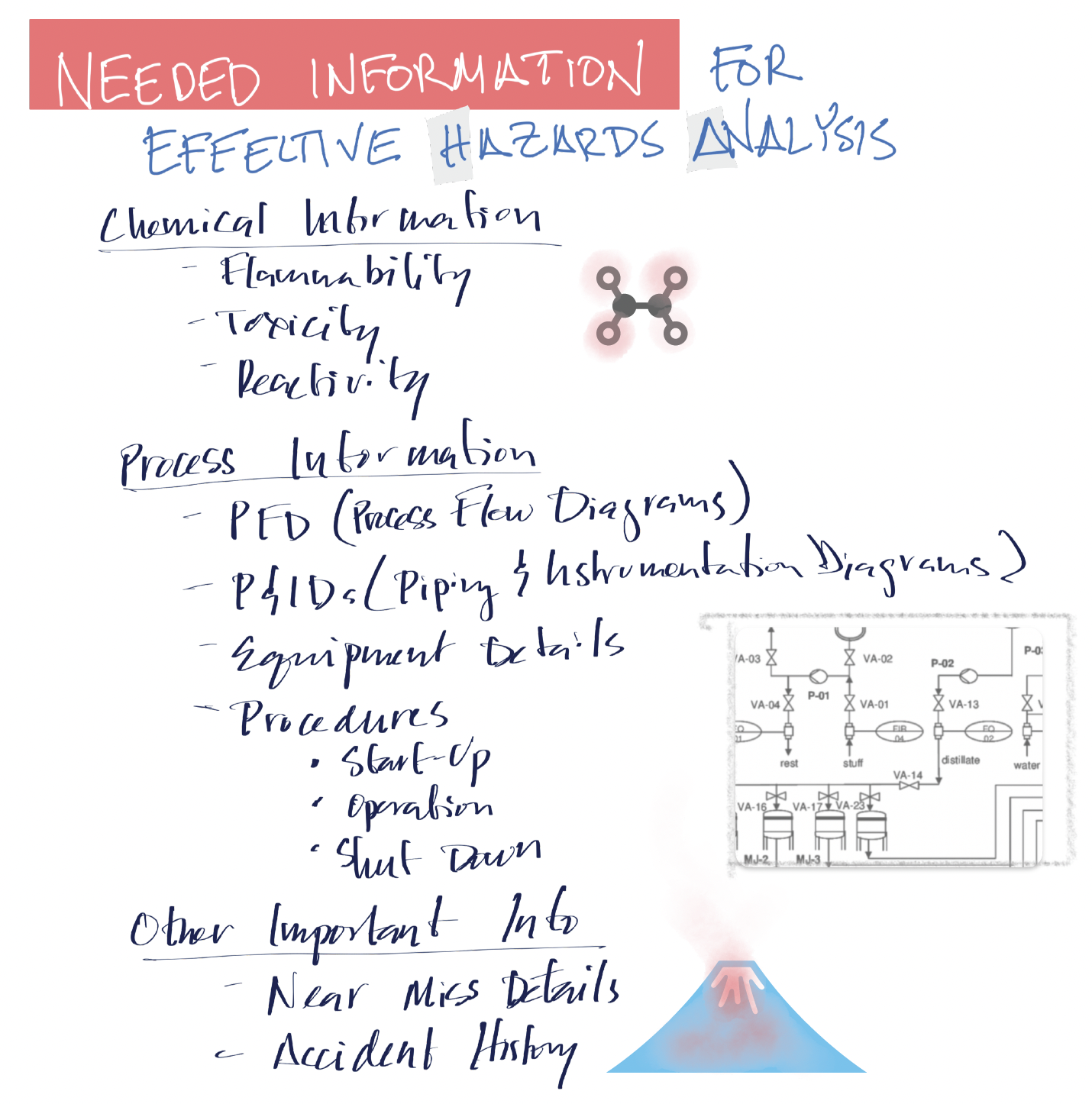
Figure 3:Needed Information for Effective Hazards Analysis
Other helpful graphics for hazards analysis and review download pdf:
physical