This section provides an overview of human body systems and toxicology, which are essential for understanding how injuries occur. It covers the anatomy and physiology of major body systems, as well as the principles of toxicology, including dose-response relationships and exposure routes.
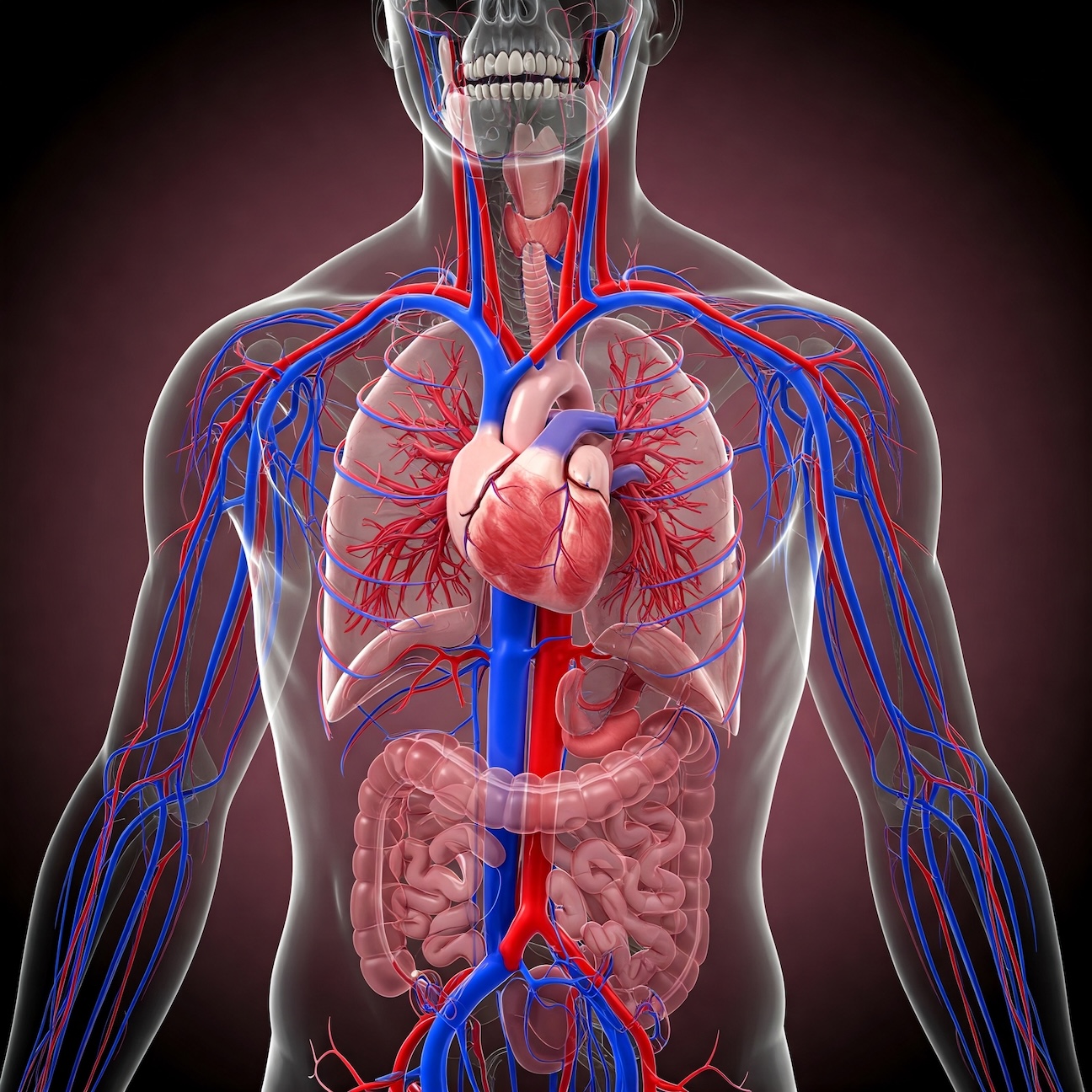
Figure 1:AI generated image of parts of the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems.
| Human Body System | Common Injury Modes |
|---|---|
| Muscular, skeletal | Slips, trips, falls, heavy or awkward lifting of objects, falling objects, machine crushing or cutting, high-speed or high-energy debris, blast or pressure waves, or blast fragment |
| Integumentary (skin, ears, eyes) | Cuts, thermal burns, chemical burns, noise, damage to eyes |
| Nervous, circulatory, digestive, respiratory, excretory, endocrine, reproductive, lymphatic, microbiome | Chemical interactions upon absorption through the skin, inhalation, ingestion, or injection |
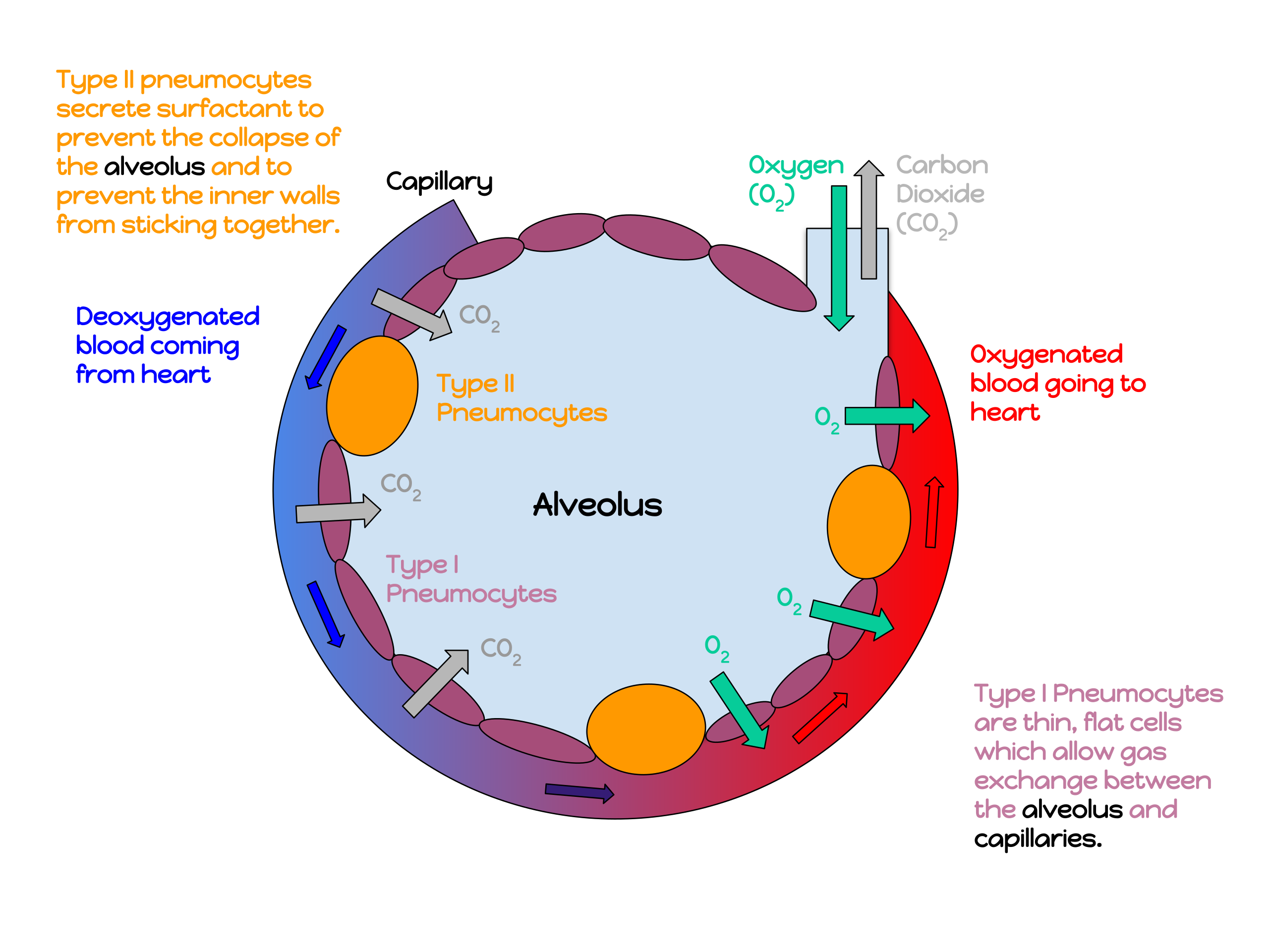
Figure 2:Un adapted image of an alveolus: a 200 micron diameter air sac found in the bronchi of the lungs. Credit to Katherinebutler1331, used per the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
Chemical Lethality¶
import numpy as np; import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
from scipy.stats import norm
#create a dataframe with the data
df = pd.DataFrame([100,200,400,800], columns=['Dose (mg/kg)'])
df['Fraction (Death)'] = [0/6,1/6,4/6,6/6]
#set function for fitting with curve_fit
def cumulative_gaussian(x, mu, sigma):
return norm.cdf(x, mu, sigma)
# fit a cumulative gaussian to the data
popt, pcov = curve_fit(cumulative_gaussian, df['Dose (mg/kg)'], df['Fraction (Death)'],p0=[350, 100])
x = np.linspace(0, 800, 100)
y = cumulative_gaussian(x, *popt)
#plot the data and the fit
df.plot(x='Dose (mg/kg)', y='Fraction (Death)', kind='scatter')
plt.plot(x, y, label='fit'); plt.grid()
plt.show()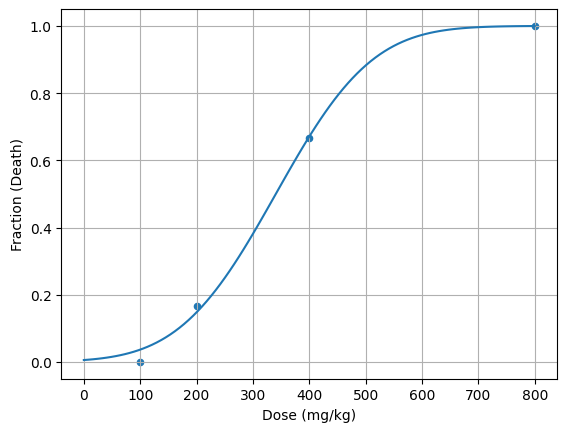
Y = scipy.stats.norm.ppf() + 5
where Y is the probit value and is the mortality fraction of probability.
Thought Experiment¶
Roll two dice (you can do that virtually here: https://
Roll the dice 5 times and count how many times you get a sum less than 3
Roll the dice 5 times and count how many times you get a sum of 3 to 5
Roll the dice 5 times and count how many times you get a sum 5 to 12
Plot the results.